MAT102 Lecture 21
-
If you're injective and bijective, you can have an invertible function.
- Injective:
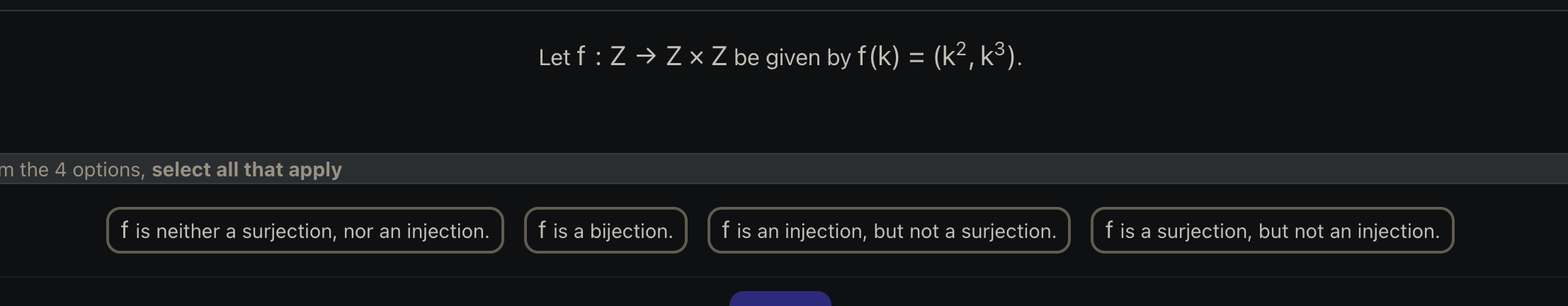
- Injective:
-
Injective Proof
- Suppose
- so then
- So them
and - So since
we know that - Why? because a negative will remain negative, so it's not like
where we lose the negative numbers. - Here we prove that we have two inputs. So then we prove that if we have two inputs, and they're the same output, then the input was the same.
- provingt it's a one-to-one function.
-
Surjective Counterexample
- Let
. There is no such that and - So it's not surjective
-
For every theory about injectivity, there's a dual theory about surjectivity
-
If
and are functions and is surjective then: - Show
is surjective - To show this, let
be arbitrary. - Since
is surjective, there - If
then , then is surjective. - Plug into
and get out.
- Show
-
Why does
not need to be surjective? - Not that
- So
- This is surjective, the composition.
- So
is surjective. - But
isn't surjective, cause we cannot take all and get everything in .
-
as - If
is injective, then is injective - proof
- Suppose
is injective, let - Thus
and - If
is injective, then becaus e - If you have one injective component, then everything is injective.
- Suppose
- So
- If
and are surjective, then is surjective. - Let
- Let
- We can't have
because says that it must be . is injective but neither or are injective - Both individually aren't injective, they don't pass the horizontal line test
- but
- If
- 1: Suppose that
is a function - a: Show that for every
- If
then the image of is - If
then - We know that
- If
let this be - So
- If
- b: Give an explicit example of a function
such that the above inclusion is strict; that is, - let
- Let the image
- Then evaluating the image we get:
- Since the image is
and the pre-image is . - Then we have that
because but .
- let
- c: Show that
is injective is injective if and only if the image is a subset of the domain, and the image is exactly the preimage of the image. - If
is injective then if we have - If
is one-to-one.
- If
- a: Show that for every
Solution
- a
- Note that
- Suppose
, so so
- Note that
- b
- Show in general that they're not always equal
- Let
- Let
- So that
- The image of
is still because we square the and get our range.
- The image of
- The preimage:
- So we know that
- c
- Suppose
is injective - Want to show that the preimage of the image of
is a subset of - Let
so if for some . - So let
- By injectivity,
, because the results are equal. - Done
- Suppose
- Contrapositive
- Suppose if
is not injective - Thus there are
but - Two points mapping to the same thing
- Let
so that - Thus,